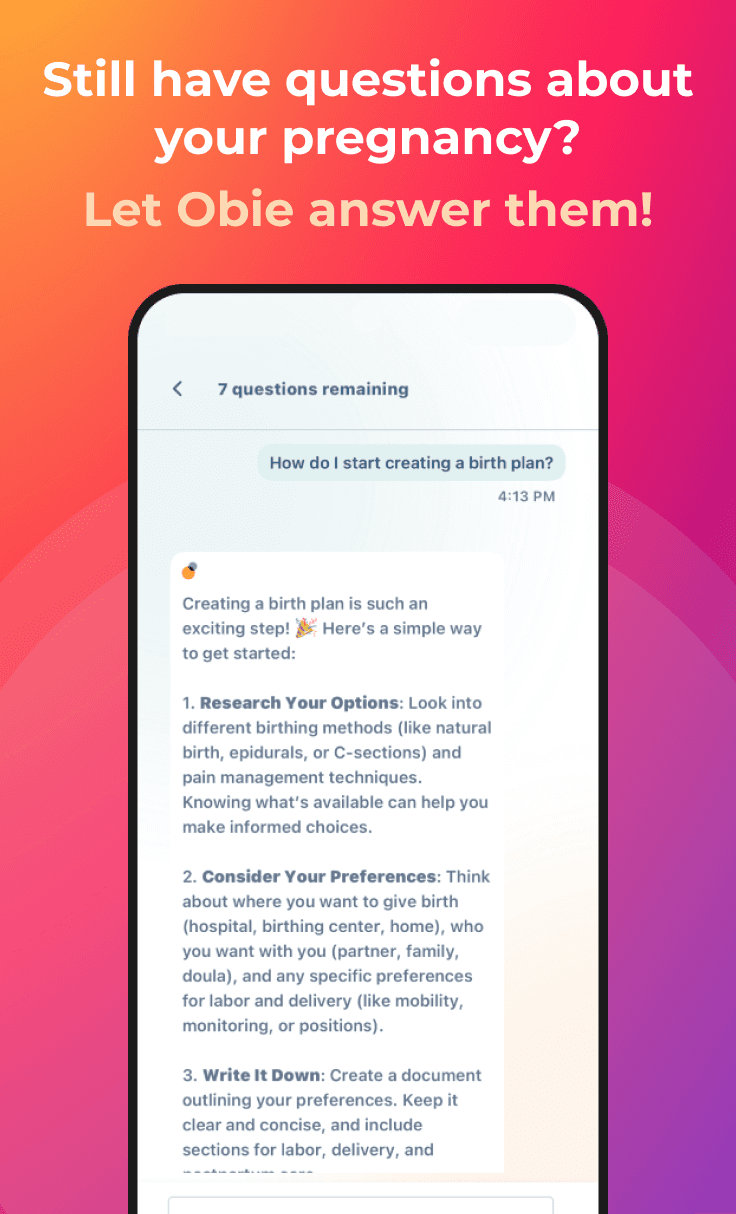
What Prenatal Tests Should I Have?
Prenatal Testing
Obie Editorial Team
Q: What prenatal tests should I have done?
A: The following is a list of recommended prenatal tests:
Ultrasound: A test in which high-frequency sound waves are used to produce an image of your baby. Ultrasound is used early in pregnancy to determine viability (if the baby is in the uterus and if the baby's heart is beating), the presence of more than one fetus, and to determine your baby's due date or gestational age (the age of the fetus). Later in pregnancy, ultrasound may be used to see how the baby is doing, to determine placenta location and the amount of amniotic fluid around the baby.
Quad Marker Screen: A blood test in which substances in the blood sample are measured to screen for problems in the development of the fetus' brain, spinal cord and other neural tissues of the central nervous system (neural tube) such as spina bifida or anencephaly. Neural tube defects occur in 1 or 2 out of every 1,000 births. The quad marker screen can detect approximately 75-80% of open neural tube defects.
The quad marker screen can also detect genetic disorders such as Down syndrome, a chromosomal abnormality. The quad marker screen can detect approximately 75% of Down syndrome cases in women under age 35 and over 80% of Down syndrome cases in women age 35 years and older.
The quad marker screen may be performed between the 15th and 20th weeks of pregnancy.
First Trimester Screen: A newer test done between weeks 10-14 detects the presence of 2 markers in a blood sample in conjunction with an ultrasound to measure the thickness of the back of the fetus' neck. It tests for chromosomal abnormalities, like Down syndrome. It is essentially as accurate as the quad marker screen but results can be obtained earlier in the pregnancy.
Amniocentesis: Amniocentesis is a procedure in which a small amount of amniotic fluid is removed from the sac surrounding the fetus and tested for birth defects. While it does not detect all birth defects, it can be used to detect sickle cell disease, cystic fibrosis, muscular dystrophy, Tay-Sachs disease or Down syndrome if the parents have a significant genetic risk.
Amniocentesis can also detect certain neural tube defects (where the spinal cord or brain don't develop normally) such as spina bifida and anencephaly. Because ultrasound is performed at the time of amniocentesis, it may detect birth defects that are not detected by amniocentesis (such as cleft palate, cleft lip, club foot or heart defects). There are some birth defects, however, that will not be detected by either amniocentesis or ultrasound.
Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS): A test in which a small sample of cells (called chorionic villi) is taken from the placenta where it attaches to the wall of the uterus. Chorionic villi are tiny parts of the placenta that are formed from the fertilized egg, so they have the same genes as the fetus. If you have certain risk factors, you may be offered CVS as a way to detect birth defects during early pregnancy. CVS requires appropriate genetic counseling, including a detailed discussion regarding the risks and benefits of the procedure.