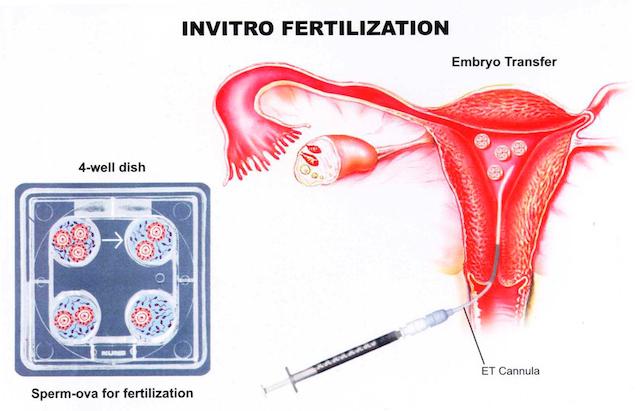
What is the usual in-vitro fertilization process?
An average in-vitro fertilization (IVF) cycle involves several steps:
- Preparation of the uterus and ovary
- Stimulation of the ovaries
- Collection of eggs (egg retrieval)
- Fertilized of the egg with sperm
- Creation of embryos in the laboratory.
What is a fresh embryo transfer?
With a fresh embryo transfer, the embryo transfer is performed in the same cycle, shortly after the fertilization, usually either three or five days after the retrieval.
What is a frozen embryo transfer?
In a frozen embryo transfer cycle, the embryo has been previously created, one or more months and sometimes even years earlier. It was then frozen, and kept frozen until it is thawed defrosted and transferred into the uterus.
Preparing the lining of the uterus for transfer
The endometrium or the lining of the uterus needs to be prepared so that the embryo can more easily implant after the transfer. The endometrium is usually checked with an ultrasound to see if it has an appropriate thickness and quality. With a fresh transfer, the estrogen already made by the ovarian follicles helps to prepare the endometrium. With a frozen transfer, patients may use estrogen patches, pills, or shots to help the endometrium. Sometimes patients may not use any medications.
Why frozen versus fresh embryo transfer?
Frozen embryo transfers have been increasing over the last years. There are several reasons why a patient may choose or be encouraged by their IVF clinician to consider a frozen embryo transfer. One of the most common reasons for a frozen embryo transfer is that the patient has leftover embryos from a fresh cycle. If a patient doesn't get pregnant, has a pregnancy loss, or has had a baby but would like another, they can use the extra embryos that have been previously created.
There may be other factors that may lower the chance of getting pregnant with a fresh transfer, thus making a frozen transfer a good option. These factors may include concern for worsening ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome if a patient conceives with a fresh transfer, elevation of progesterone during ovarian stimulation, leading to concern that the embryo and the uterus are out of sync. Patients planning genetic testing of the embryos usually need to freeze the embryos while waiting for test results. Finally, if there is an issue with the endometrium, such as a polyp or a thin endometrium, the transfer may be canceled until the uterus can be evaluated completely.
The chance of pregnancy is about the same for fresh or frozen embryo transfer
The technology used to freeze and thaw embryos has advanced such that the likelihood of the embryo surviving the process is very high. So this has led many people to wonder which is better fresh or frozen. Should we be doing one or the other for all patients?
The answer, at least for now is that generally, the chance of getting pregnant with a fresh or frozen embryo may be about the same but it also depends on several circumstances.
Study fresh versus frozen embryos
A recent study of over eighty thousand IVF cycles looked at pregnancy rates and the chance of having a baby between women having fresh and frozen embryo transfers. They looked at different types of patients.
- Women who were high responders had more than 14 eggs retrieved
- Intermediate responders had six to fourteen eggs retrieved.
- Low responders had less than 6 eggs retrieved.
High responders had a higher chance of pregnancy and live birth with a frozen cycle. If women have fewer eggs retrieved, she was more likely to have a pregnancy or baby with a fresh transfer.
Other differences between fresh and frozen embryos
In a frozen cycle, the hormonal environment may be more physiologically similar to a pregnancy conceived without any infertility treatment. So the pregnancy outcomes may be more likely to be normal. Some studies have demonstrated that pregnancies from a frozen embryo transfer are less likely to be an ectopic pregnancy or result in preterm delivery. Also, the babies seem to be less likely to have low birth weight or be small for gestational age. Some people speculate that the differences seen between fresh and frozen transfers are related to the fact that the woman's hormonal environment is very different in a fresh IVF cycle due to the ovarian stimulation.
Calculate your IVF success rates HERE.
Reference: Acharya KS et al. Freezing of all embryos in in-vitro fertilization is beneficial in high responders, but not intermediate and low responders: an analysis of 82,935 cycles from the Society for Assisted Reproductive Technology registry. Fertil Steril. 2018 Oct;110(5):880-887.
