Premature Rupture of Fetal Membranes - PROM
Obie Editorial Team
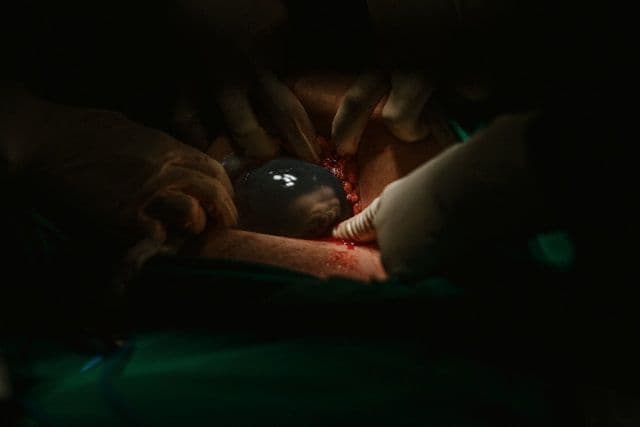
Premature rupture of fetal membranes (PROM) is an event where the protective amniotic sac, surrounding your baby, breaks before the onset of labor. It’s crucial to understand that the approach to handling PROM varies depending on how many weeks pregnant you are when it occurs, along with any other pregnancy complications such as potential infections.
The amniotic sac is like a secure cocoon for your baby, shielding against infections from bacteria or viruses. When labor is imminent, the amniotic fluid, often called “water,” breaks, indicating that your baby is preparing to journey through the birth canal into the world.
What Happens When PROM Occurs?
In some instances, this “water breaking” can occur before labor naturally begins, a situation referred to as premature rupture of fetal membranes (PROM). PROM can manifest post 37 weeks (term PROM) or pre-37 weeks (preterm PROM or PPROM). An important aspect to remember is that a rupture in the amniotic sac increases the risk of infection for both you and your baby.
The exact cause for PROM isn’t always evident, but there is a notable link between PROM and certain pre-existing infections.
Whatever the cause, healthcare providers will follow standardized protocols for managing PROM. These protocols revolve around when during your pregnancy PROM occurs and if there are other complicating factors.
Management Based on Gestational Age:
- **Term PROM (after 37 weeks):** In this case, the risks associated with infections overshadow any risks related to the baby’s prematurity. The typical recommendation by healthcare providers is to proceed with delivery.
- **Preterm PROM (before 37 weeks):** If PROM happens between 34-37 weeks, delivery is usually advised due to higher infection risks.
- **Very Preterm PROM (before 32-34 weeks):** If there are no signs of infection or complications, doctors often opt to wait, allowing more time for the baby’s development. During this period, antibiotics are generally administered, alongside medications to enhance the maturity of the baby’s lungs and other vital organs.
Immediate Steps to Take:
Once the membranes rupture, it’s imperative to contact your obstetrician immediately. Admission to the hospital is often necessary for monitoring and management. Notably, many instances of PROM will lead to labor within 24 hours. If spontaneous labor does not commence, and the pregnancy is beyond 34 weeks, labor induction via medication is often considered. Antibiotics are a vital part of care to prevent infections for both you and your baby, though delivering the baby becomes essential to ensure overall safety.
Monitoring PROM Before 34 Weeks:
For cases of PROM before 34 weeks without immediate labor, careful monitoring is necessary to keep an eye on signs of infection and the baby’s well-being.
Nature’s Timing or a Medical Concern?
Remember, while premature rupture of membranes can sometimes signal that labor is approaching soon, at other times it may result from other factors like a weak spot in the amniotic sac. Following the rupture, most mothers give birth within days. Yet, in cases of earlier gestational age, waiting might be the suitable option if there are no signs of complications, allowing your baby the gift of more time to mature.
Continue to communicate openly and promptly with your healthcare team. You’re equipped with the knowledge to navigate this scenario proactively.