Ovarian Cysts Fertility and Pregnancy
Medical Problems
Obie Editorial Team
Q: Will ovarian cysts impair fertility or have an adverse effect on pregnancy?
What is an ovarian cyst?
An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled space inside or on top of the ovary. They can exist in one or both ovaries. Ovarian cysts are unique in that they can be attributed to a number of other conditions. The origin, as well as the type of ovarian cyst, is an important factor in determining whether or not you will be able to conceive naturally or have problems during pregnancy.
Types of ovarian cysts
Ovarian cysts can be simple or complex, depending on the way they appear on a sonogram. Simple cysts are fluid-filled spaces, while complex ovarian cysts are those that contain either blood or a solid substance. In addition, the size of the cyst is important when determining the treatment.
What is a follicle cyst?
A follicle cyst is a fluid-filled cyst that is often normal as it happens right before and after ovulation in the space of the ovary from where the egg was ejected. This sac is located inside the ovaries. In most cases, this follicle or sac breaks open and releases an egg. However, if the follicle doesn’t break open, the fluid inside the follicle can form a cyst on the ovary.
What is a corpus luteum cyst?
Most follicle cysts usually dissolve after the release an egg. Although, if the sac doesn’t dissolve and the opening of the follicle seals, additional fluid can develop inside the sac, and this accumulation of fluid causes a corpus luteum cyst. A corpus luteum cyst can happen during pregnancy and is usually not a serious problem unless it grows to a significant size.
What is a dermoid cyst?
A dermoid cyst is a sac-like growth on the ovaries that can contain hair, fat, and other tissue. It usually requires removal, especially if it grows too large.
What is a cystadenomas?
A cystadenoma is a cyst, a noncancerous growth which can develop on the outer surface of the ovaries.
What is an endometrioma?
Endometrial tissue normally grows inside the uterus. However, it can also grow outside the uterus and attach to other organs including the ovaries, which results in a cyst.
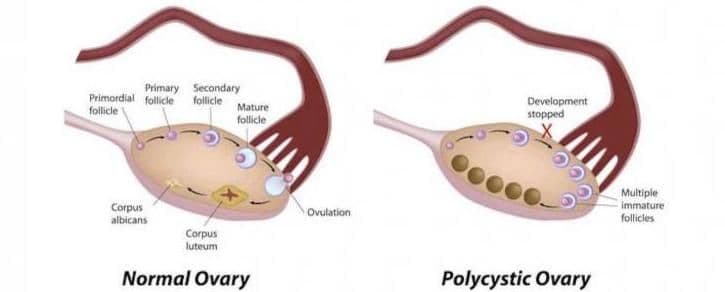
PCOS and ovarian cysts
If the ovarian cyst is linked to PCOS or polycystic ovarian syndrome, there can be issues with conceiving. PCOS is linked to a series of symptoms rather than one definitive diagnosis. The patient will present with irregular periods, lack of periods, infertility, excess body weight and possibly increased body hair. As a whole, these symptoms backed with ultrasound and hormone testing can lead to the diagnosis of PCOS. This condition can also cause ovarian cysts and if so, fertility is often compromised.
Ovarian cysts can also be linked to endometriosis. Fertility is not commonly affected by this condition, but it is affected by pregnancy. The only time a woman with endometriosis feels complete relief is during her pregnancy as the condition disappears. There is no known cure for endometriosis, often referred to as a benign cancer, aside from a complete hysterectomy. If the endometriosis has grown into the ovaries and fallopian tubes fertility could be affected once the condition has gone unnoticed to this point.
An ovarian cyst discovered during pregnancy will not usually have an effect on the pregnancy unless it grows big, looks suspicious or if there are symptoms. If the cyst continues to grow, torsion can occur. Torsion is the twisting of the cyst to the point of extreme pain. Most often, this pain is treated with pain medications until after the baby is born.
Read More