What Is A Bicornuate Uterus?
Gynecology
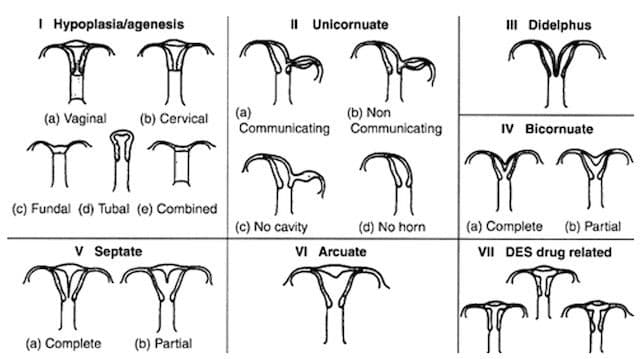
A bicornuate uterus is the most common congenital uterine anomaly and can impact a woman's reproductive capabilities. In the U.S., it is estimated that bicornuate uterus is seen in 1-5/1,000 women, though this may be an underestimate since not all are diagnosed, especially when they are not severe.
A bicornuate uterus is an abnormality of the uterus that has two horns and a heart shape. The uterus has a wall inside and a partial split outside. If necessary, a bicornuate uterus can be corrected surgically. Few studies of the surgery have been published. In three studies reporting on a total of 11 women, approximately 90% successfully carried a pregnancy to term.
Several studies show that women with a bicornuate uterus have about a 60% success rate in delivering a living child but have a higher risk of cervical incompetence. The condition is associated with an increased rate of spontaneous abortion, though the miscarriage rate is lower with a bicornuate uterus than with a septate uterus. That's probably because the blood supply to the midline indentation is better. Premature labor, a breech presentation and/or a retained or trapped placenta are also common complaints with a bicornuate uterus.
Diagnostic Procedures
A bicornuate uterus can be confirmed through use of the following techniques:
- Pelvic exam: Two horns can occasionally be palpated.
- Sonogram: A bicornuate uterus can sometimes be diagnosed by ultrasound
- Laparoscopy: Provides information on the exterior shape of the uterus.
- Hysteroscopy: Provides information on the interior configuration of the uterus.
Treatment
Metroplasty surgery: To create a large uterine cavity with minimal destruction of uterine tissue is the treatment of choice.
Cervical cerclage: Improved the fetal survival rate in selected patients. Both metroplasty and a cervical cerclage may be prescribed.
Pregnancy Outcome With Bicornuate Uterus And Other Anomalies
| Live Birth | Preterm Birth | Ectopic | Miscarriage | |
| Arcuate Uterus | 66.2% | 5.1% | 3.6% | 20.1% |
| Uterine Septum | 58.1% | 10% | 1.9% | 75.7% |
| Bicornuate Uterus | 62.5% | 25% | 0 | 25% |
| Didelphic Uterus | 68.6% | 24.4% | 2.3% | 20.9% |
| Unicornuate Uterus | 54.2% | 43.3% | 4.3% | 34.4% |
| Controls | 82% | 9-12% | 2% | 10-15% |
References:
Raga. Hum Reprod 1997;12:2277
Fedele. Eur J Obstet Gynaecol 1995
J Womens Health 2004